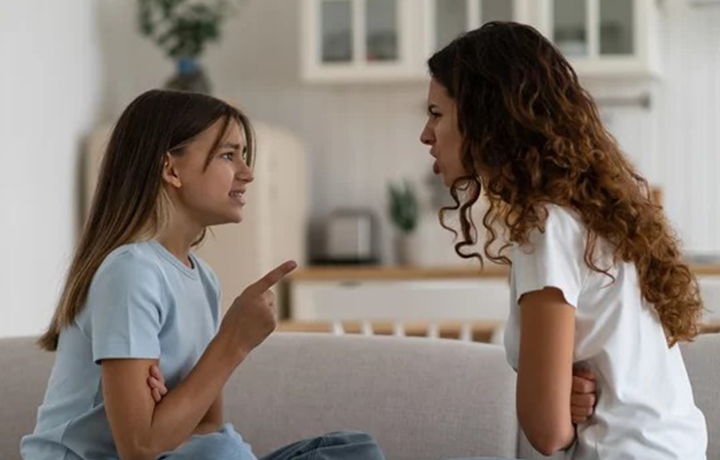
Adolescence is a period marked by significant physical, emotional, and social changes, often leading to heightened anger and frustration. Understanding the root causes and effective strategies for managing adolescent anger is crucial for parents and caregivers.
Understanding Adolescent Anger
- Triggers of Anger: Anger in adolescents can be triggered by a perceived violation of their well-being, such as feeling misunderstood, embarrassed, or mistreated. Adolescents are particularly sensitive to changes and challenges in their self-image, social status, and autonomy.
- Functions of Anger: Anger serves two primary functions:
- Protective: It highlights violations of personal boundaries or well-being, prompting corrective action.
- Expressive: It provides an outlet for expressing dissatisfaction and seeking change.
- Developmental Changes: Adolescents often experience more frequent and intense anger due to the rapid physical, emotional, and social changes they undergo. This can include challenges with self-image, peer relationships, and autonomy.
Strategies for Parents
- Empathetic Listening: Instead of responding with anger, parents should practice empathetic listening to understand the underlying causes of their adolescent’s anger.
- Encouraging Communication: Open, non-judgmental communication can help adolescents articulate their feelings and work through their anger constructively.
- Modeling Behavior: Parents should model healthy anger management techniques, demonstrating how to handle frustration calmly and effectively.
- Providing Support: Access to counseling and support groups can be beneficial for adolescents struggling with anger issues. Professional guidance can help them develop coping mechanisms and resilience.
Practical Tips
- Identify Triggers: Help adolescents identify what triggers their anger and develop strategies to manage these situations.
- Promote Problem-Solving: Encourage adolescents to think through their anger and find constructive solutions to their problems.
- Teach Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and physical activity can help adolescents manage their anger.
- Foster Positive Relationships: Supportive relationships with family and peers can provide a buffer against the stressors that contribute to anger.
Managing adolescent anger requires a combination of understanding, empathy, and practical strategies. By creating a supportive and communicative environment, parents can help their adolescents navigate this challenging period and develop healthy ways to express and manage their emotions.






